Lb
Resource Icon
Resource Overview
Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances. It also monitors the health of registered targets and routes traffic only to healthy targets. Elastic Load Balancing supports three types of load balancers: Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer, and Classic Load Balancer. Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances. It also monitors the health of registered targets and routes traffic only to healthy targets. Elastic Load Balancing supports three types of load balancers: Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer, and Classic Load Balancer.
Associated Resources
Parent Resources
Connected Resources
Resource Setting Values
Basic Settings
load_balancer_type: ELB type -application,network,gatewayinternal: Deploy ELB as internet-facing or internal -true,falseincluded_vpc_name: Name of the VPC where target resources are createdlinked_subnet_names: List of subnet names connected to the load balancerlinked_security_group_names: List of security group names assigned to the load balancer (Application LB only)drop_invalid_header: Whether to drop invalid HTTP headers -true,false
Listener (listener)
listener.protocol: Protocol between client and load balancer -HTTP,HTTPS,TCP,TCP_UDP,TLS,UDPlistener.port: Port on which the load balancer listenslistener.default_action_type: Default routing action type -forward,redirect,fixed-responselistener.linked_target_group_name: Name of the target group to route traffic tolistener.acm_certificate_name: Name of the default SSL server certificatelistener.ssl_policy: Name of the SSL policy applied to the listener
Listener Rules (rule)
rule.target_listener: Listener name to apply the rule torule.priority: Rule priority -1~50000
Fixed Response (rule.fixed_response)
rule.fixed_response.fixed_response_order: Fixed response priority -1~50000rule.fixed_response.content_type: Response content typerule.fixed_response.message_body: Response message bodyrule.fixed_response.fixed_response_status_code: HTTP response status code
Forward (rule.forward)
rule.forward.forward_order: Forward priority -1~50000rule.forward.forward_target_group_list: List of target groups for forwardingrule.forward.enable_stickiness: Whether target group stickiness is enabled -true,falserule.forward.duration: Duration (seconds) traffic is routed to the same target group
Redirect (rule.redirect)
rule.redirect.redirect_order: Redirect priority -1~50000rule.redirect.host: Host name (supports#{host})rule.redirect.path: Absolute path (must start with/)rule.redirect.port: Port -1~65535or#{port}rule.redirect.protocol: Protocol -HTTP,HTTPS,#{protocol}rule.redirect.query: Query stringrule.redirect.redirect_status_code: HTTP redirect code -HTTP_301,HTTP_302
Authentication (rule.authenticate)
rule.authenticate.authenticate_type: Authentication type -authenticate_cognito,authenticate_oidcrule.authenticate.authenticate_order: Authentication priority -1~50000rule.authenticate.on_unauthenticated_request: Action for unauthenticated requests -deny,allow,authenticaterule.authenticate.scope: User scope requested from the IdPrule.authenticate.session_cookie_name: Cookie name used for session persistencerule.authenticate.session_timeout: Session duration (seconds) -60~86400rule.authenticate.user_pool_arn: Cognito User Pool ARNrule.authenticate.user_pool_client_id: Cognito User Pool Client IDrule.authenticate.user_pool_domain: Cognito User Pool domainrule.authenticate.authorization_endpoint: IdP authorization endpointrule.authenticate.client_id: OAuth 2.0 Client IDrule.authenticate.client_secret: OAuth 2.0 Client Secretrule.authenticate.issuer: OIDC issuerrule.authenticate.token_endpoint: Token endpointrule.authenticate.user_info_endpoint: User info endpoint
Conditions (rule.condition)
condition_list: List of rule conditions to usehost_header: Host header condition valuepath_pattern: Path pattern condition valuehttp_request_method: HTTP method condition valuehttp_header_name: HTTP header namehttp_header_value: HTTP header valuequery_string_key: Query string keyquery_string_value: Query string valuesource_ip: Source IP condition value
Tags
tag: Tags used to categorize the resource - maximum 512 characters,key:value
LB Configuration Guide
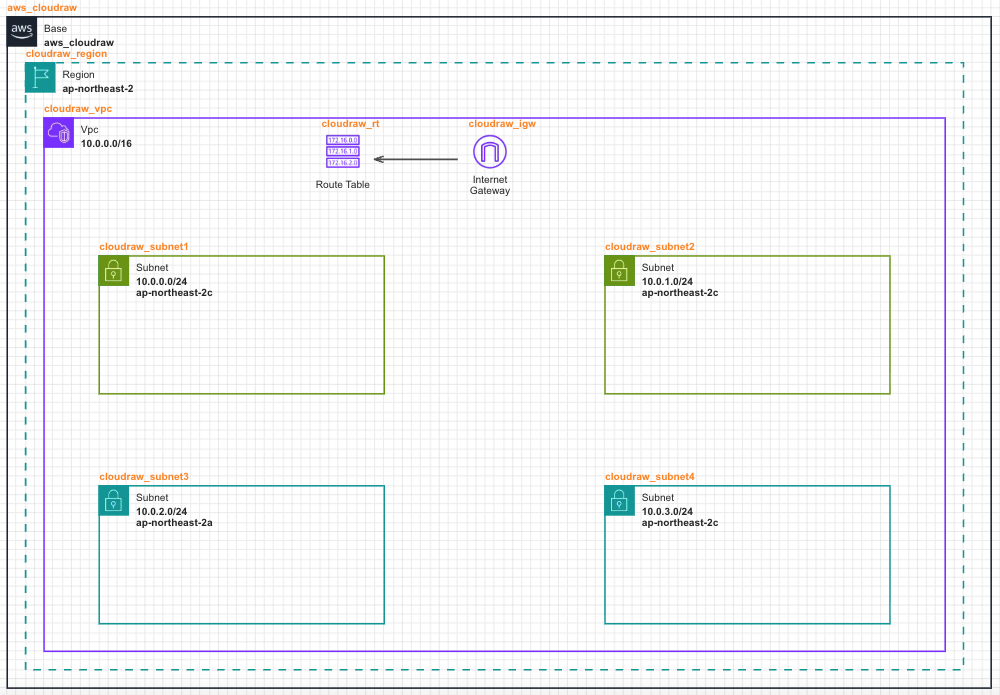
- This guide explains how to configure a Load Balancer based on an environment where Base → Region → VPC → Subnet → Internet Gateway → Route Table have already been placed.
- Refer to Subnet and configure the top two Subnets as Public Subnets.
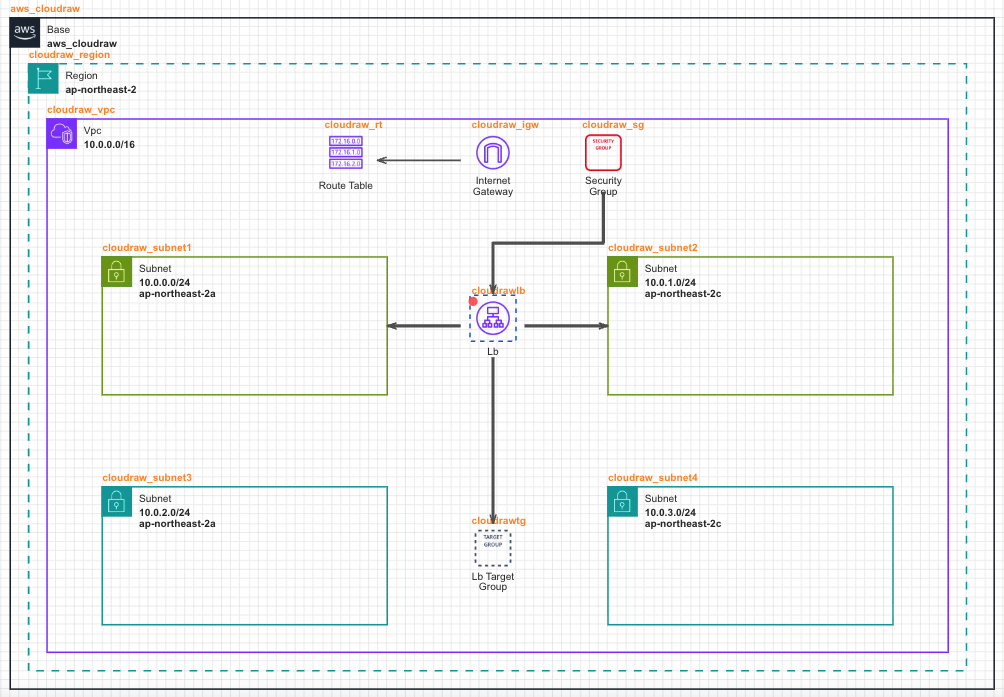
- Place a Security Group and connect it to the Load Balancer.
- To receive external requests through a single entry point and distribute traffic across multiple EC2 instances, place a Load Balancer and connect it to Public Subnets configured in different Availability Zones.
- To define the set of target resources to which the Load Balancer will forward traffic, place a Load Balancer Target Group and connect it in the [Load Balancer -> Load Balancer Target Group] direction.
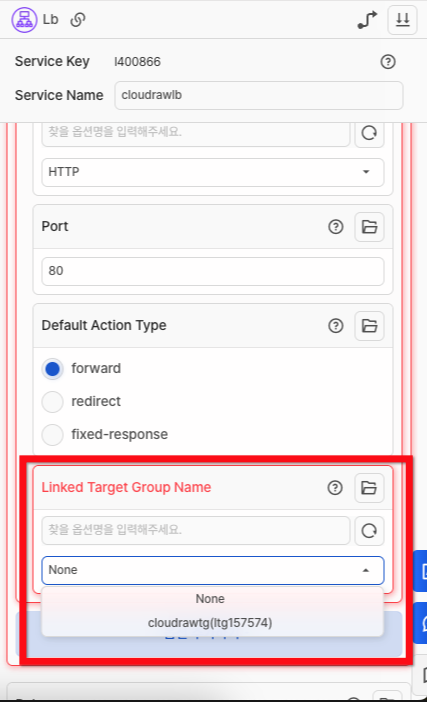
- In the Load Balancer [Listener - Linked Target Group Name] option, select the name of the connected Load Balancer Target Group.
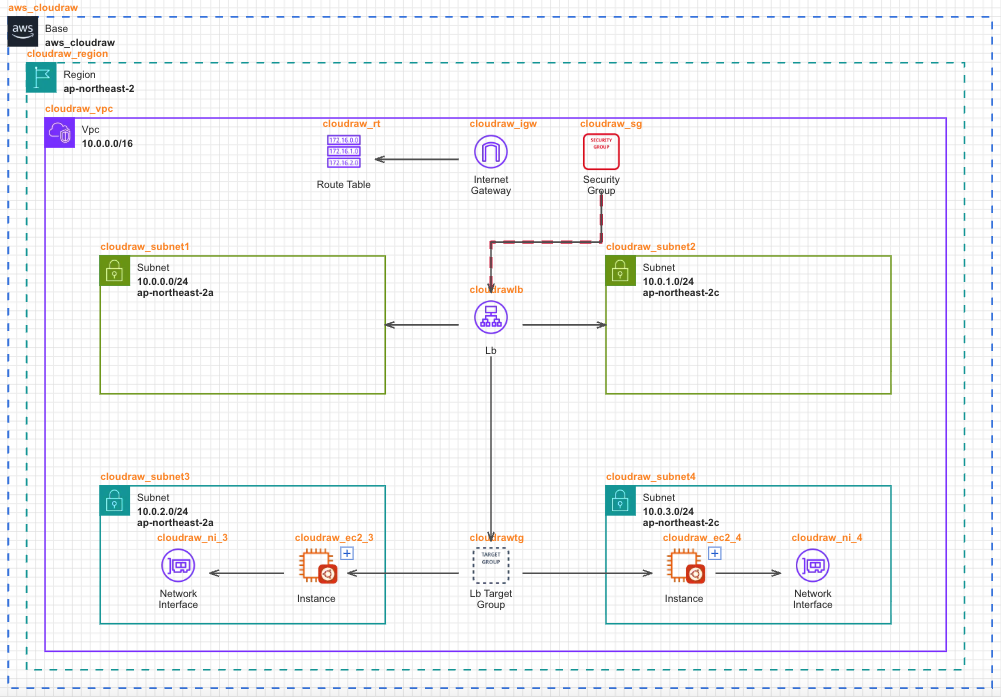
- Place EC2 Instances and Network Interfaces in the Private Subnet area, then configure the AMI for the EC2 instances.
- Connect the Load Balancer Target Group to the EC2 instances that will handle actual traffic, allowing the Load Balancer to distribute requests appropriately.